In 2018, nine states reported an adult obesity prevalence at or above 35 percent: Alabama, Arkansas, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, and West Virginia. This comes from the new obesity prevalence maps released last week by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The maps break down adult obesity prevalence by race, ethnicity, and location based on self-reported height and weight data.
Highlights:
- Obesity prevalence ranged from 23.0 percent in Colorado to 39.5 percent in Mississippi and West Virginia
- Combined data from 2016-2018 showed notable differences by race and ethnicity:
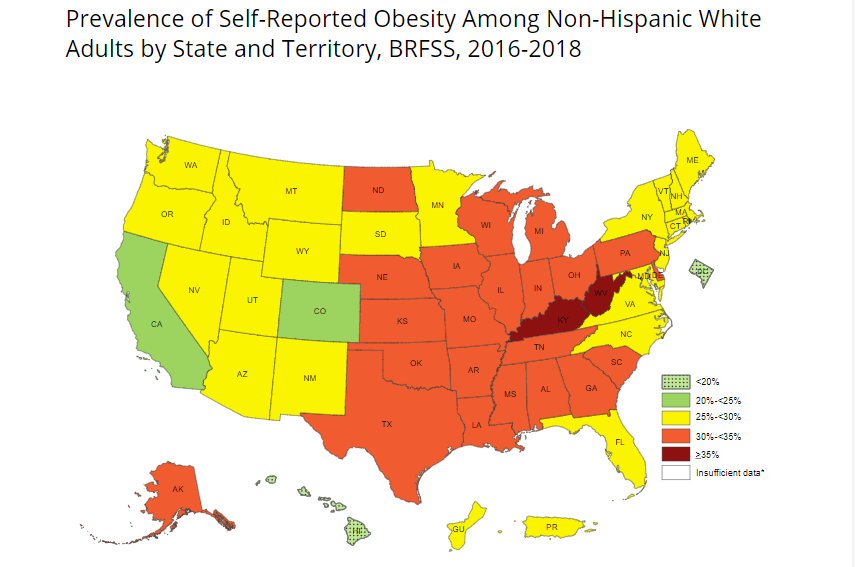
- 2 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic white adults
- 9 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among Hispanic adults
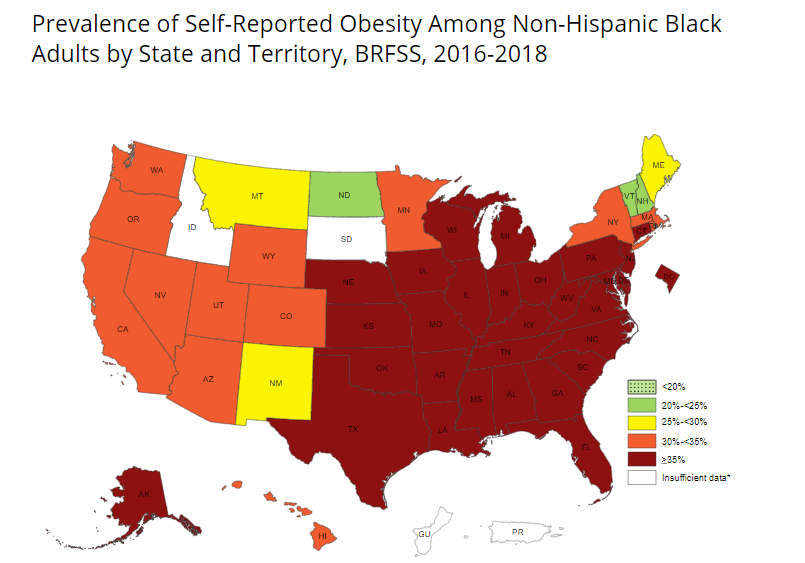
- 29 states and the District of Columbia had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic black adults.
- Obesity decreased by level of education. Adults without a high school degree or equivalent had the highest self-reported obesity (35.0%), followed by high school graduates (33.1%), adults with some college (33.0%) and college graduates (24.7%).
- Young adults were half as likely to have obesity as middle-aged adults. Adults aged 18-24 years had the lowest self-reported obesity (18.1%) compared to adults aged 45-54 years who had the highest prevalence (36.9%).
Story continues below
- All states and territories had more than 20% of adults with obesity.
- 20% to less than 25% of adults had obesity in 2 states (Colorado and Hawaii) and the District of Columbia.
- 25% to less than 30% of adults had obesity in 17 states and Guam.
- 30% to less than 35% of adults had obesity in 22 states and Puerto Rico.
- 35% or more adults had obesity in 9 states (Alabama, Arkansas, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, and West Virginia).
- The South (33.6%) and the Midwest (33.1%) had the highest prevalence of obesity, followed by the Northeast (28.0%), and the West (26.9%).
Adults with obesity are at increased risk for many serious health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, some cancers, and poorer mental health. Obesity costs the United States health care system over $147 billion a year. In addition, research has shown that obesity affects work productivity and military readiness.
Turning the tide on obesity will take a comprehensive effort by all parts of society. These maps help by showing where the burden of obesity is greatest. Factors like neighborhood design; access to healthy, affordable foods and beverages; and access to safe and convenient places for physical activity can all impact obesity.


Bulloch Public Safety
02/27/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Chattooga Opinions
Deborah Devotions: Praising God

Chattooga Local News
Summerville 10U Team Disqualified After Eligibility Ruling Based on 2022 Lease

Bulloch Public Safety
02/26/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/09/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/16/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/20/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/17/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/02/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County