July is National Sarcoma and Bone Cancer Awareness Month!
What is bone cancer?
Bone cancer is a type of cancer that occurs when the cells in our bones start to grow out of control. Most bone cancers fall into a specific category of tumors known as sarcomas. A sarcoma is a cancerous tumor that affects the bone and soft tissues (such as muscles and nerves)
There are two main types of bone cancer: primary bone cancer and metastatic bone cancer. Primary bone cancer occurs when cancer originates in the bone itself. On the other hand, metastatic bone cancer occurs when cancer spreads to the bones from other organs in the body. This can result from many other types of cancer (such as lung, breast, prostate, etc.). Metastatic cancer is far more common than primary bone cancer—accounting for 99% vs. 1% of bone cancer diagnoses, respectively.
How prevalent is bone cancer?
Bone cancer is extremely rare. In 2022, the American Cancer society estimates that there will be 3,910 new cases of primary bone cancer and 2,100 related deaths. This only accounts for 0.2% and 0.3% of total U.S. cancer cases and deaths, respectively.
There are many types of primary bone cancer, but the three most common forms are osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma.
Osteosarcoma (or osteogenic sarcoma) is the most common type of primary bone cancer. It often occurs in young adults (ages 10-30).
Chondrosarcoma is the second most common type of primary bone cancer. It is rare in individuals under the age of 20 and older individuals bear the highest risk of developing the disease.
Finally, Ewing sarcomas (or Ewing tumors) are the third most common type of primary bone cancer. This cancer is rare in adults over the age of 30 and most commonly affects children, teens, and young adults. How is bone cancer diagnosed?
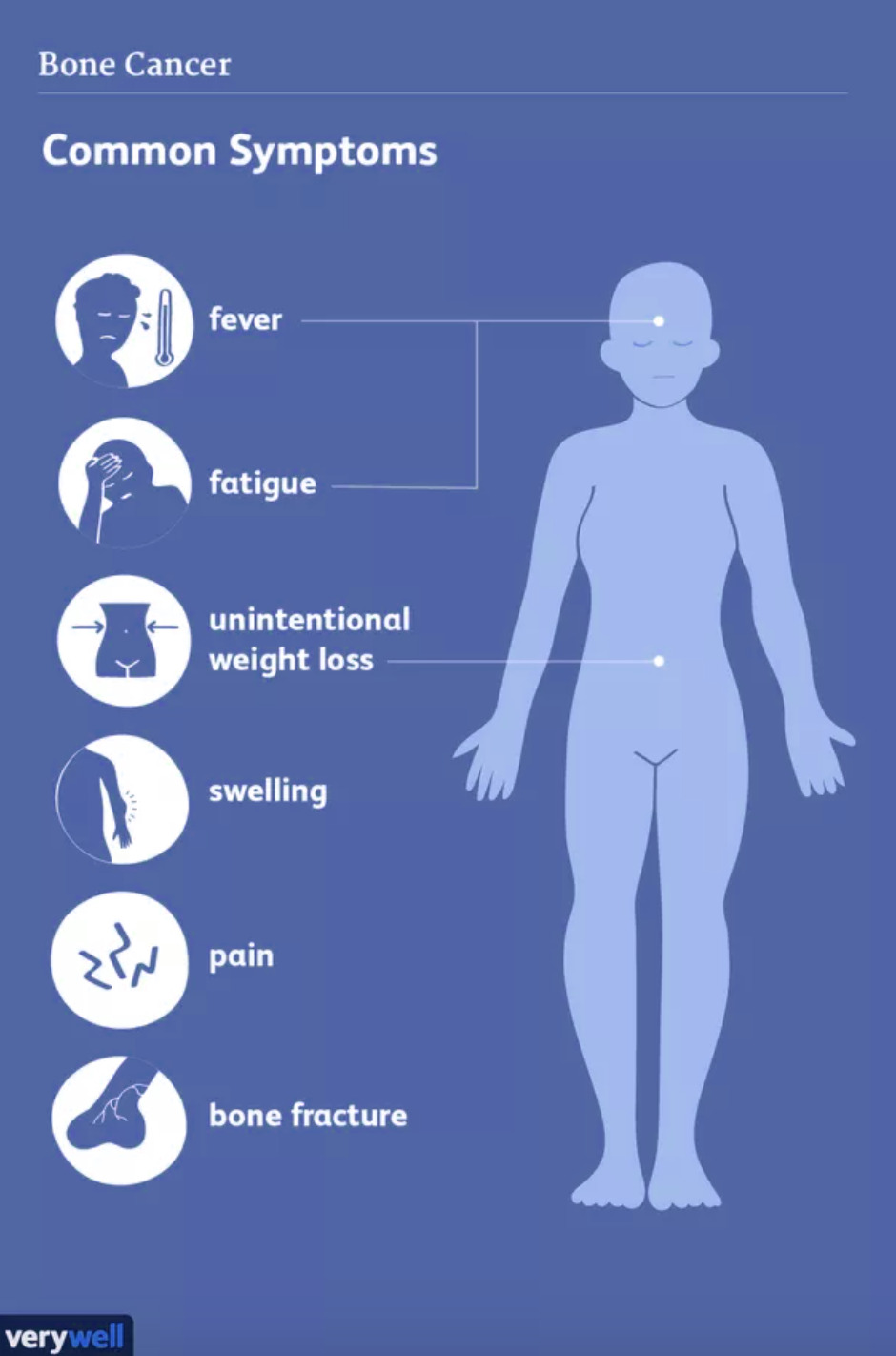
Because of its rare and ambiguous nature, bone cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Many of the symptoms of bone cancer are more likely to be related to other common conditions, such as arthritis or physical injuries. Despite this, it is important to be aware of common bone cancer symptoms and to seek help from a physician if these ailments persist for long periods of time.
If bone cancer is suspected, various tests and screening procedures can be used to officially diagnose the disease. These methods include, but are not limited to:
· Imaging (X-Ray/MRI/CT/PET/Bone Scans)
· Biopsies (Surgical or Needle)
· Blood Tests/Labs
· Medical History/Physical Exams
For more information on bone cancer, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options, visit the American Cancer Society resource page.