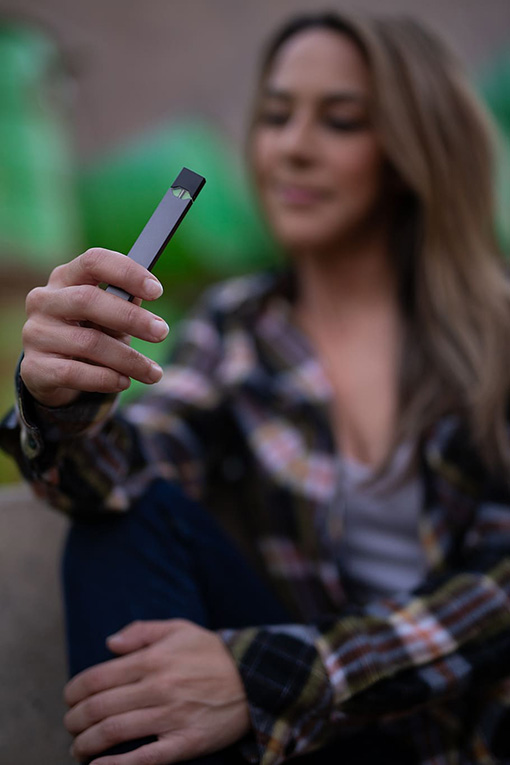
Attorney General Chris Carr announced a $438.5 million agreement in principle between JUUL Labs (“JUUL”) and 34 states and territories resolving a two-year bipartisan investigation into the e-cigarette manufacturer’s marketing and sales practices. In addition to the financial terms, the settlement would force JUUL to comply with a series of strict injunctive terms severely limiting the company’s marketing and sales practices. Under the settlement, more than $19 million has been allocated for payment to the State of Georgia.
“For two years, we have worked with a bipartisan coalition of attorneys general to learn all of the facts associated with JUUL’s marketing to minors,” said Carr. “Underage vaping has reached epidemic proportions, and our office is committed to protecting Georgia’s youth from products that could be harmful to their health. That includes holding accountable those that unlawfully try to sell dangerous and addictive e-cigarettes to minors in our state.”
JUUL was, until recently, the dominant player in the vaping market. The multistate investigation revealed that JUUL rose to this position by willfully engaging in an advertising campaign that appealed to youth, even though its e-cigarettes are both illegal for them to purchase and are unhealthy for youth to use. The investigation found that JUUL relentlessly marketed to underage users with launch parties, advertisements using young and trendy-looking models, social media posts and free samples. It marketed a technology-focused, sleek design that could be easily concealed and sold its product in flavors known to be attractive to underage users. JUUL also manipulated the chemical composition of its product to make the vapor less harsh on the throats of young and inexperienced users. To preserve its young customer base, JUUL relied on age verification techniques that it knew were ineffective.
The investigation further revealed that JUUL’s original packaging was misleading in that it did not clearly disclose that it contained nicotine and implied that it contained a lower concentration of nicotine than it actually did. Consumers were also misled to believe that consuming one JUUL pod was the equivalent of smoking one pack of combustible cigarettes. The company also misrepresented that its product was a smoking cessation device without FDA approval to make such claims.
The states are in the process of finalizing and executing the settlement documents – a process that takes approximately three to four weeks. The $438.5 million would be paid out over a period of six to 10 years, with the amounts paid increasing the longer the company takes to make the payments. If JUUL chooses to extend the payment period up to 10 years, the final settlement would reach $476.6 million. Both the financial and injunctive terms exceed any prior agreement JUUL has reached with states to date.
As part of the settlement, JUUL has agreed to refrain from:
- Youth marketing
- Funding education programs
- Depicting persons under age 35 in any marketing
- Use of cartoons
- Paid product placement
- Sale of brand name merchandise
- Sale of flavors not approved by FDA
- Allowing access to websites without age verification on landing page
- Representations about nicotine not approved by FDA
- Misleading representations about nicotine content
- Sponsorships/naming rights
- Advertising in outlets unless 85 percent audience is adult
- Advertising on billboards
- Public transportation advertising
- Social media advertising (other than testimonials by individuals over the age of 35, with no health claims)
- Use of paid influencers
- Direct-to-consumer ads unless age-verified
- Free samples
The agreement also includes sales and distribution restrictions, including where the product may be displayed/accessed in stores, online sales limits, retail sales limits, age verification on all sales, and a retail compliance check protocol.
In addition to Georgia, the following states have also signed on to the agreement: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Maine, Mississippi, Montana, North Dakota, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Nevada, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Puerto Rico, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Vermont, Wisconsin and Wyoming.


Chattooga Opinions
Medically Supervised Weight Loss: Inside Premier Weight Loss & Medispa

Chattooga Local News
Georgia Power Files Plan for Customer Rate Decrease with Public Service Commission

Chattooga Local Government
Carr Pushes for Permanent Halt of Medicare and Medicaid Funding for Child Sex-Change Procedures

Bulloch Public Safety
02/20/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
01/26/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/09/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/16/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/02/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
01/30/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County