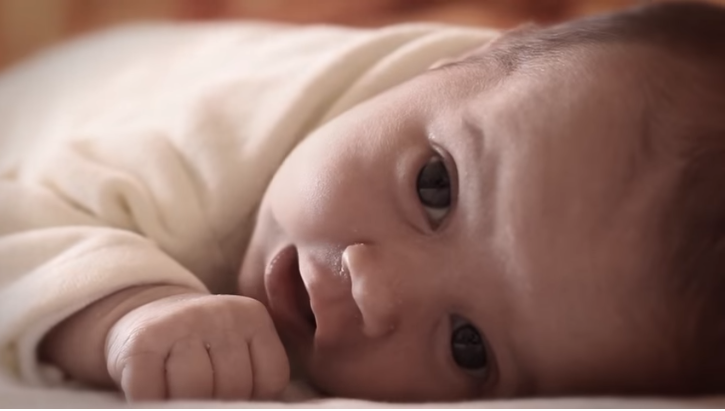
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has released two Informational Bulletins, Caring Recovery for Infants and Babies (CRIB) and Help for Moms and Babies (HMB). These Bulletins discuss certain provisions of the Substance-Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act (SUPPORT Act) that provide new coverage options to state Medicaid programs to assist some of the most vulnerable beneficiaries – babies, pregnant women, and mothers – with Substance Use Disorder (SUD), including opioid use disorder (OUD).
Fighting the opioid epidemic continues to be a top priority for the Trump Administration, and CMS is committed to helping states ensure that mothers and children have access to care at a variety of facilities by offering a framework of new choices states may use to help infants, and pregnant and postpartum women affected by the opioid crisis. The CRIB and HMB provisions of the SUPPORT Act add to existing efforts that work to address treatment for pregnant and postpartum women with SUD, including OUD, and for infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), such as CMS’s Integrated Care for Kids (InCK) and Maternal Opioid Misuse (MOM) Models.
“The opioid epidemic has affected the entire country, but the impact on babies is one of the most tragic consequences of this public health crisis,” said CMS Principal Deputy Administrator for Operations and Policy Kimberly Brandt. “Our comprehensive efforts to combat the opioid epidemic include a laser focus on the needs of vulnerable populations, and today’s Bulletins build on our previous efforts to support moms and children struggling with the impact of opioid use disorder.”
Last year, CMS released a Bulletin, “Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: A Critical Role for Medicaid in the Care of Infants,” to provide states with information about current studies on treatment and other considerations when designing approaches to treatment of infants with NAS, including Medicaid coverage options and limitations.
The SUPPORT Act provision discussed in the CRIB Bulletin added an option for states to pay for services at a new provider type, Residential Pediatric Recovery Center (RPRC), for treatment of infants with NAS without any other significant medical risk factors. RPRCs can offer mothers and caregivers counseling, referrals for other services, activities to encourage caregiver-infant bonding, and training on infant care.
The SUPPPORT Act provision discussed in the HMB Bulletin creates a new limited exception to the Institution for Mental Disease (IMD) exclusion for certain pregnant and postpartum women. Specifically, states may receive federal matching funds for services provided outside of an IMD to eligible pregnant and post partum women, such as prenatal services and other services to ensure the safe delivery of the baby.
This is a press release from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services


Bulloch Public Safety
03/06/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Chattooga Local Government
“Adopt a Dispatcher” from Walker County for National Public Safety Telecommunicators Week

Chattooga Schools
Pirelli North America donates to Longleaf Pine Restoration

Chattooga Local News
Georgia Named “Rising Star” in National Childhood Index

Bulloch Public Safety
02/09/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/16/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
03/02/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/20/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County

Bulloch Public Safety
02/17/2026 Booking Report for Bulloch County